Implementations of Advanced Data Structures
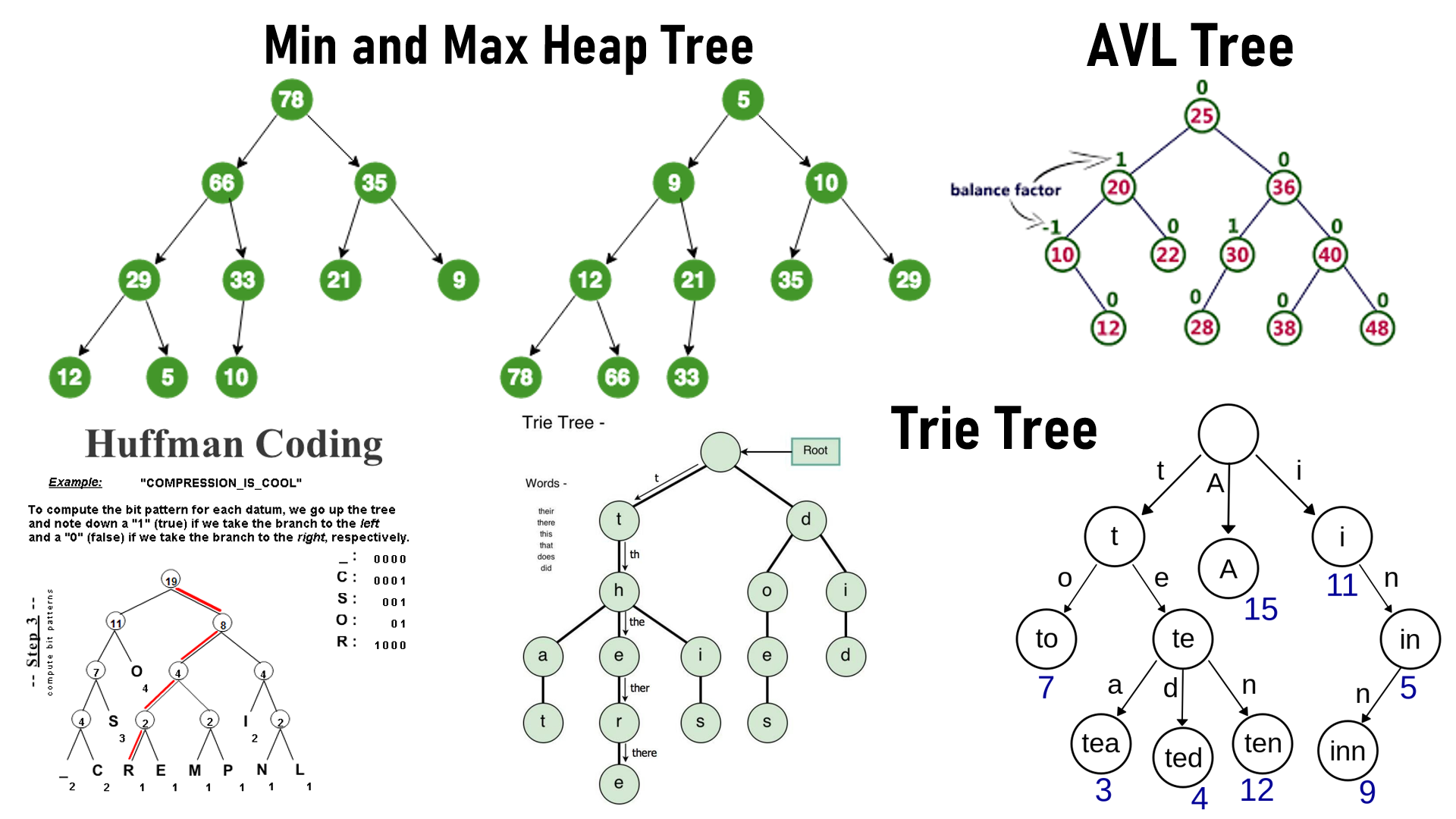
Implemented AVL Tree, Min Heap, Huffman Code Tree and Prefix Tree
Median Finder with AVL Tree
This C++ program implements a median finder using an AVL tree data structure. It allows you to efficiently find the median of a sequence of integers as they are inserted one by one.
Overview
This program reads integers from the standard input and inserts them into an AVL tree. As each integer is inserted, it calculates and maintains the median of the integers seen so far. The median calculation is based on the AVL tree’s ability to efficiently find the element at a specified rank (position) in logarithmic time.
Features
- Efficient insertion of integers into an AVL tree.
- Real-time median calculation as integers are inserted.
- Support for both odd and even-length sequences of integers.
k-Closest Points using Heap
This C++ program finds the k closest points to the origin (0,0) from a given set of points using a min-heap data structure. It allows you to efficiently determine the closest points based on their Euclidean distances from the origin.
Overview
The program reads the number of points (n) and the value of k from the standard input. It then reads n points (x, y) and uses a min-heap to keep track of the k closest points. The distance of each point from the origin is calculated as (�2+�2).
Features
- Efficiently find the k closest points from a set of n points.
- Utilizes a min-heap to maintain the closest points.
- Works with points in 2D space.
Huffman Coding
This C++ program implements Huffman coding, a widely-used lossless data compression algorithm. Huffman coding is used to encode and decode data efficiently, with shorter codes assigned to more frequently occurring characters. This program takes a set of characters and their frequencies as input and generates a Huffman coding tree. It then encodes and decodes messages using the generated Huffman codes.
Overview
The program reads the following input:
- Number of characters (n).
- For each character:
- The character itself (e.g., ‘A’).
- Its frequency of occurrence in the message.
The program constructs a Huffman tree based on the character frequencies and encodes a given message using the generated Huffman codes. It can also decode a message encoded with the same Huffman codes.
Features
- Huffman coding tree construction.
- Encoding of messages using Huffman codes.
- Decoding of messages encoded with Huffman codes.
- Efficient data compression and decompression.
Prefix Tree
This C++ program implements a prefix tree, also known as a trie. A trie is a tree-like data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve a dynamic set of strings or keys. In this program, the trie is used to store a set of binary strings and count the occurrence of each unique binary string.
Overview
The program reads the following input:
- Number of binary strings (n).
- For each binary string:
- The binary string itself.
The program constructs a trie (prefix tree) based on the input binary strings and counts the occurrence of each unique binary string. It then prints the unique binary strings along with their counts.
Features
- Trie (prefix tree) construction.
- Counting the occurrence of unique binary strings.
- Efficient storage and retrieval of binary strings.